ChatGPT as a tool for posing of mathematical problems by prospective teachers
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.31129/LUMAT.14.1.2942Keywords:
problem posing, algebraic reasoning, teacher training, ChatGPTAbstract
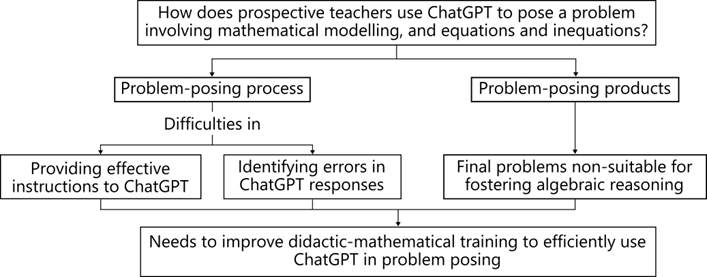
Problem posing is a fundamental competence of the mathematics teacher, which motivates the interest in including this activity in teacher training plans. Incorporating problem posing into teaching practice involves considering the tools available to the teacher for this purpose, in particular generative artificial intelligence programs such as ChatGPT. This article analyzes how prospective teachers use ChatGPT to pose a problem involving mathematical modeling and equations and inequalities. The results highlight the difficulties of prospective teachers in providing effective instructions and identifying errors in ChatGPT responses. The problems that were finally proposed by the prospective teachers were, for the most part, not suitable for fostering algebraic reasoning. The joint analysis of the interaction of prospective teachers with ChatGPT and their final problem proposal made it possible to detect shortcomings in relation to their didactic-mathematical knowledge of algebraic reasoning and, in particular, of modeling. We conclude that using ChatGPT for posing mathematical problems has potential in teacher training, but didactic-mathematical training is needed for efficiently using this tool to elaborate meaningful problems.
References
Alsina, Á., Pincheira, N., & Delgado-Rebolledo, R. (2024). The professional practice of designing tasks: How do pre-service early childhood teachers promote mathematical processes in early algebra? ZDM – Mathematics Education, 56(6), 1197–1210. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11858-024-01636-1 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11858-024-01636-1
Alsina, Á., & Salgado, M. (2021). Introduciendo la Modelización Matemática Temprana en Educación Infantil: Un marco para resolver problemas reales. Modelling in Science Education and Learning, 14(1), 33. https://doi.org/10.4995/msel.2021.14024 DOI: https://doi.org/10.4995/msel.2021.14024
Australian Curriculum, Assessment and Reporting Authority (ACARA). (2014). Foundation to year 10 curriculum: Number sense and algebra (ACMSPO24).
Ayllón, M. F., Gallego, J. L., & Gómez, I. A. (2016). La actuación de estudiantes de educación primaria en un proceso de invención de problemas. Perfiles Educativos, 38(152), 51–67. https://doi.org/10.22201/iisue.24486167e.2016.152.57588 DOI: https://doi.org/10.22201/iisue.24486167e.2016.152.57588
Baumanns, L., & Rott, B. (2021). Rethinking Problem-Posing Situations: A Review. Investigations in Mathematics Learning, 13(2), 59–76. https://doi.org/10.1080/19477503.2020.1841501 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/19477503.2020.1841501
Borromeo, R. (2018). Learning How to Teach Mathematical Modeling in School and Teacher Education. Springer International Publishing. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-68072-9 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-68072-9
Burgos, M., Tizón-Escamilla, N., & Chaverri, J. (2025). A model for problem creation: Implications for teacher training. Mathematics Education Research Journal, 37(1), 55–84. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13394-023-00482-w DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13394-023-00482-w
Cai, J., & Hwang, S. (2020). Learning to teach through mathematical problem posing: Theoretical considerations, methodology, and directions for future research. International Journal of Educational Research, 102, 101391. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijer.2019.01.001 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijer.2019.01.001
Cai, J., & Leikin, R. (2020). Affect in mathematical problem posing: Conceptualization, advances, and future directions for research. Educational Studies in Mathematics, 105(3), 287–301. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10649-020-10008-x DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10649-020-10008-x
Cooper, G. (2023). Examining Science Education in ChatGPT: An Exploratory Study of Generative Artificial Intelligence. Journal of Science Education and Technology, 32(3), 444–452. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10956-023-10039-y DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10956-023-10039-y
Core State Standards Initiative [CCSSI]. (2015). Common Core State Standards for Mathematics.
Dogan, M. F. (2020). Evaluating Pre-Service Teachers’ Design of Mathematical Modelling Tasks. International Journal of Innovation in Science and Mathematics Education, 28(1), 44–59. https://doi.org/10.30722/ijisme.28.01.004 DOI: https://doi.org/10.30722/IJISME.28.01.004
Elgrably, H., & Leikin, R. (2021). Creativity as a function of problem-solving expertise: Posing new problems through investigations. ZDM – Mathematics Education, 53(4), 891–904. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11858-021-01228-3 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11858-021-01228-3
English, L. D. (2020). Teaching and learning through mathematical problem posing: Commentary. International Journal of Educational Research, 102, 101451. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijer.2019.06.014 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijer.2019.06.014
Farrokhnia, M., Banihashem, S. K., Noroozi, O., & Wals, A. (2024). A SWOT analysis of ChatGPT: Implications for educational practice and research. Innovations in Education and Teaching International, 61(3), 460–474. https://doi.org/10.1080/14703297.2023.2195846 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/14703297.2023.2195846
Fernández, M. E., & Carrillo, J. (2020). Uma aproximação à forma como os alunos do ensino primário formulam problemas. Revista de Educação Matemática, 17, e020015. https://doi.org/10.37001/remat25269062v17id257 DOI: https://doi.org/10.37001/remat25269062v17id257
Getenet, S. (2024). Pre-service teachers and ChatGPT in multistrategy problem-solving: Implications for mathematics teaching in primary schools. International Electronic Journal of Mathematics Education, 19(1), em0766. https://doi.org/10.29333/iejme/14141 DOI: https://doi.org/10.29333/iejme/14141
Godino, J. D., Giacomone, B., Batanero, C., & Font, V. (2017). Enfoque Ontosemiótico de los Conocimientos y Competencias del Profesor de Matemáticas. Bolema: Boletim de Educação Matemática, 31(57), 90–113. https://doi.org/10.1590/1980-4415v31n57a05 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1590/1980-4415v31n57a05
Godino, J. D., Neto, T., Wilhelmi, M. R., Etchegaray, S., & Lasa, A. (2015). Algebraic reasoning levels in primary and secondary education. In K. Krainer & N. Vondrová, Proceedings of the Ninth Congress of the European Society for Research in Mathematics Education (pp. 426–432). CERME.
Hansen, R., & Hana, G. M. (2015). Problem Posing from a Modelling Perspective. In F. M. Singer, N. F. Ellerton, & J. Cai (Eds), Mathematical Problem Posing: From Research to Effective Practice (pp. 35–46). Springer New York. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4614-6258-3_2 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4614-6258-3_2
Hartmann, L.-M., Krawitz, J., & Schukajlow, S. (2022). The process of modelling-related problem posing—A case study with preservice teachers. In C. Fernández, S. Linares, Á. Gutiérrez, & N. Planas (Eds), Proceedings of the 45th Conference of the International Group for the Psychology of Mathematics Education (Vol. 2, pp. 355–362). PME.
Hartmann, L.-M., Krawitz, J., & Schukajlow, S. (2023). Posing and Solving Modelling Problems—Extending the Modelling Process from a Problem Posing Perspective. Journal Für Mathematik-Didaktik, 44(2), 533–561. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13138-023-00223-3 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13138-023-00223-3
Kieran, C. (2022). The multi-dimensionality of early algebraic thinking: Background, overarching dimensions, and new directions. ZDM – Mathematics Education, 54(6), 1131–1150. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11858-022-01435-6 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11858-022-01435-6
Leavy, A., & Hourigan, M. (2022). The Framework for Posing Elementary Mathematics Problems (F-PosE): Supporting Teachers to Evaluate and Select Problems for Use in Elementary Mathematics. Educational Studies in Mathematics, 111(1), 147–176. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10649-022-10155-3 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10649-022-10155-3
Ledezma, C., Rodríguez-Nieto, C. A., & Font, V. (2024). The Role Played by Extra-mathematical Connections in the Modelling Process. Avances de Investigación En Educación Matemática, 25, 81–103. https://doi.org/10.35763/aiem25.6363 DOI: https://doi.org/10.35763/aiem25.6363
Liljedahl, P., & Cai, J. (2021). Empirical research on problem solving and problem posing: A look at the state of the art. ZDM – Mathematics Education, 53(4), 723–735. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11858-021-01291-w DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11858-021-01291-w
Lodico, M. G., Spaulding, D. T., & Voegtle, K. H. (2010). Methods in educational research: From theory to practice. Wiley.
Malaspina, U., Mallart, A., & Font, V. (2015). Development of teachers’ mathematical and didactic competencies by means of problem posing. In K. Krainer & N. Vondrová (Eds), Proceedings of the Ninth Congress of the European Society for Research in Mathematics Education (pp. 2861–2866). Charles University in Prague, Faculty of Education and ERME.
Malaspina, U., Torres, C., & Rubio, N. (2019). How to Stimulate In-Service Teachers’ Didactic Analysis Competence by Means of Problem Posing. In P. Liljedahl & L. Santos-Trigo (Eds), ICME-13 Monographs (pp. 133–151). Springer International Publishing. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-10472-6_7 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-10472-6_7
Mallart, A., Font, V., & Diez, J. (2018). Case Study on Mathematics Pre-service Teachers’ Difficulties in Problem Posing. EURASIA Journal of Mathematics, Science and Technology Education, 14(4). https://doi.org/10.29333/ejmste/83682 DOI: https://doi.org/10.29333/ejmste/83682
Memarian, B., & Doleck, T. (2023). ChatGPT in education: Methods, potentials, and limitations. Computers in Human Behavior: Artificial Humans, 1(2), 100022. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chbah.2023.100022 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chbah.2023.100022
Ministerio de Educación y Formación Profesional [MEFP]. (2022). Real Decreto 157/2022, de 1 de marzo, por el que se establecen la ordenación y las enseñanzas mínimas de la Educación Primaria. Boletín Oficial Del Estado, 52(I), 24386–24504.
Pelton, T., & Pelton, L. F. (2023). Adapting ChatGPT to support teacher education in mathematics. In E. Langran, P. Christensen, & J. Sanson (Eds), Proceedings of Society for Information Technology & Teacher Education International Conference (pp. 1662–1670). Association for the Advancement of Computing in Education (AACE).
Ray, P. P. (2023). ChatGPT: A comprehensive review on background, applications, key challenges, bias, ethics, limitations and future scope. Internet of Things and Cyber-Physical Systems, 3, 121–154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.iotcps.2023.04.003 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.iotcps.2023.04.003
Rudolph, J., Tan, S., & Tan, S. (2023). ChatGPT: Bullshit spewer or the end of traditional assessments in higher education? Journal of Applied Learning & Teaching, 6(1), 1–22. https://doi.org/10.37074/jalt.2023.6.1.9 DOI: https://doi.org/10.37074/jalt.2023.6.1.9
Sarrion, E. (2023). Exploring the power of ChatGPT. Applications, Techniques, and Implications. Apress Berkeley, CA. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4842-9529-8 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4842-9529-8
Silber, S., & Cai, J. (2021). Exploring underprepared undergraduate students’ mathematical problem posing. ZDM – Mathematics Education, 53(4), 877–889. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11858-021-01272-z DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11858-021-01272-z
Singer, F. M., Ellerton, N., & Cai, J. (2013). Problem-posing research in mathematics education: New questions and directions. Educational Studies in Mathematics, 83(1), 1–7. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10649-013-9478-2 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10649-013-9478-2
Stein, M. K., Grover, B. W., & Henningsen, M. (1996). Building student capacity for mathematical thinking and reasoning: An analysis of mathematical tasks used in reform classrooms. American Educational Research Journal, 33(2), 455–488. https://doi.org/10.3102/00028312033002455 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3102/00028312033002455
Stohlmann, M. S., & Albarracín, L. (2016). What Is Known about Elementary Grades Mathematical Modelling. Education Research International, 8(5), 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/5240683 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/5240683
Su, J., & Yang, W. (2023). Unlocking the Power of ChatGPT: A Framework for Applying Generative AI in Education. ECNU Review of Education, 6(3), 355–366. https://doi.org/10.1177/20965311231168423 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1177/20965311231168423
Urban, M., Děchtěrenko, F., Lukavský, J., Hrabalová, V., Svacha, F., Brom, C., & Urban, K. (2024). ChatGPT improves creative problem-solving performance in university students: An experimental study. Computers & Education, 215, 105031. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2024.105031 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2024.105031
Wardat, Y., Tashtoush, M. A., AlAli, R., & Jarrah, A. M. (2023). ChatGPT: A revolutionary tool for teaching and learning mathematics. EURASIA Journal of Mathematics, Science and Technology Education, 19(7), em2286. https://doi.org/10.29333/ejmste/13272 DOI: https://doi.org/10.29333/ejmste/13272
Yao, Y., Hwang, S., & Cai, J. (2021). Preservice teachers’ mathematical understanding exhibited in problem posing and problem solving. ZDM – Mathematics Education, 53(4), 937–949. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11858-021-01277-8 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11858-021-01277-8
Zapatera, A., & Quevedo, E. (2021). The Initial Algebraic Knowledge of Preservice Teachers. Mathematics, 9(17), 2117. https://doi.org/10.3390/math9172117 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/math9172117
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
Categories
License
Copyright (c) 2026 María Burgos, Nicolás Tizón-Escamilla

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.









