Effects of online heutagogy approach in learning science via Telegram towards pupils’ science process skills and creative thinking skills
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.31129/LUMAT.12.4.2327Keywords:
Online Learning, Heutagogy, Science Process Skills, Creative Thinking Skills, TelegramAbstract
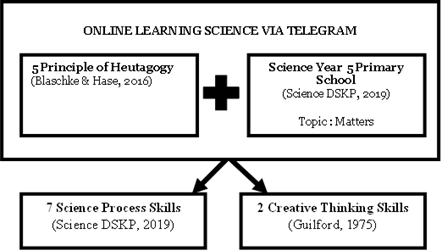
The COVID-19 pandemic has necessitated the adoption of online learning methods worldwide, including in Malaysia. The Ministry of Education (MoE) in Malaysia has recognized the importance of online learning due to the implementation of Movement Control Order (MCO). However, the limitations of online learning, such as reduced interaction between teachers and pupils, have prompted educators to explore alternative approaches that emphasize self-directed learning. Hence, this study aimed to develop a learning method based on the heutagogy approach using the Telegram platform and examine its impact on science process skills and creative Thinking Skills in primary school pupils. The study employed a quantitative research design with a pre-experimental design and involved 20 Year 5 pupils. Pre-post tests were conducted to assess the skills, and the data were analyzed using descriptive and inferential analysis techniques. The descriptive analysis revealed a mean improvement in both Science process skills and Creative Thinking Skills following the intervention with the heutagogy approach. Furthermore, the inferential analysis confirmed a significant difference between pre- and post-test scores for both skills after integrating the heutagogy approach. The positive findings of this study shed light on the efficacy of the heutagogy approach in online learning, particularly in the context of science education for primary school pupils. These results offer valuable insights to educators who can consider incorporating the heutagogy approach into their teaching practices. By doing so, educators can enhance the learning experiences and outcomes of their pupils in science education.
References
Adhiriyanthi, S., Solihin, H., & Arifin, M. (2021). Improving students’ creative thinking skills through guided inquiry practicums learning with STEM approach. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 1806(1). https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1806/1/012180 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1806/1/012180
Ahmed, V., Alzaatreh, A., & Saboor, S. (2023). Students’ Perceptions of Online Teaching in Higher Education Amid COVID-19. Journal of Science Education and Technology, 32(5), 629–642. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10956-023-10069-6 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10956-023-10069-6
Azlan, C. A., Wong, J. H. D., Tan, L. K., Muhammad Shahrun, M. S. N., Ung, N. M., Pallath, V., Tan, C. P. L., Yeong, C. H., & Ng, K. H. (2020). Teaching and learning of postgraduate medical physics using Internet-based e-learning during the COVID-19 pandemic – A case study from Malaysia. Physica Medica, 80, 10–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmp.2020.10.002 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmp.2020.10.002
Blaschke, L. M., & Hase, S. (2016). Heutagogy: A Holistic Framework for Creating Twenty-First-Century Self-determined Learners. In Lecture Notes in Educational Technology (Issue 9783662477236, pp. 25–40). Springer International Publishing. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-662-47724-3_2 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-662-47724-3_2
BPK, B. P. K. (2019). Dokumen Standard Kurikulum dan Pentaksiran (DSKP) Sains.
Bykasova, L., Kamenskaya, E., Krevsoun, M., & Podbereznyj, V. (2021). Heutagogy as a Concept of Online Education in Higher School. E3S Web of Conferences, 258. https://doi.org/10.1051/e3sconf/202125807073 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1051/e3sconf/202125807073
Canning, N. (2010). Playing with heutagogy: Exploring strategies to empower mature learners in higher education. Journal of Further and Higher Education, 34(1), 59–71. https://doi.org/10.1080/03098770903477102 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/03098770903477102
Chen, L., Luan Wong, S., & How, S. P. (2023). A systematic review of factors influencing student interest in online homework. In Research and Practice in Technology Enhanced Learning (Vol. 18). DOI: https://doi.org/10.58459/rptel.2023.18039
Daut, N., & Halim, N. D. A. (2021). Effects of Online Heutagogy Learning Environment towards Students’ Creativity in English Presentation. 2021 1st Conference on Online Teaching for Mobile Education, OT4ME 2021, 138–145. https://doi.org/10.1109/OT4ME53559.2021.9638922 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/OT4ME53559.2021.9638922
Ekici, M., & Erdem, M. (2020). Developing Science Process Skills through Mobile Scientific Inquiry. Thinking Skills and Creativity, 36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tsc.2020.100658 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tsc.2020.100658
Elfeky, A. I. M., Masadeh, T. S. Y., & Elbyaly, M. Y. H. (2020). Advance organizers in flipped classroom via e-learning management system and the promotion of integrated science process skills. Thinking Skills and Creativity, 35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tsc.2019.100622 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tsc.2019.100622
Guzey, S. S., & Li, W. (2023). Engagement and Science Achievement in the Context of Integrated STEM Education: A Longitudinal Study. Journal of Science Education and Technology, 32(2), 168–180. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10956-022-10023-y DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10956-022-10023-y
Hanifah, W., & Subiyantoro, S. (2020). Creative Thinking Skills in Science Lessons in Elementary Schools. DOI: https://doi.org/10.2991/assehr.k.200129.107
Hase, S., & Kenyon, C. (2007). Semantic Play and Possibility Invited Contribution Heutagogy: A Child of Complexity Theory. In An International Journal of Complexity and Education (Vol. 4, Issue 1). www.complexityandeducation.ca DOI: https://doi.org/10.29173/cmplct8766
Hussin, F. and A. J. and N. M. S. Z. (2014). Kaedah Penyelidikan & Analisis Data SPSS. UUM Press. DOI: https://doi.org/10.32890/9789670474670
Khamhaengpol, A., Sriprom, M., & Chuamchaitrakool, P. (2021). Development of STEAM activity on nanotechnology to determine basic science process skills and engineering design process for high school students. Thinking Skills and Creativity, 39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tsc.2021.100796 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tsc.2021.100796
Kung-Teck, W., Muhammad, M. binti, Abdullah, N. binti, & Hamdan, A. (2020). Mobile-heutagogical practices among student teachers: Its pedagogical affordances and challenges. International Journal of Interactive Mobile Technologies, 14(2), 130–143. https://doi.org/10.3991/ijim.v14i02.11819 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3991/ijim.v14i02.11819
Leasa, M., Batlolona, J. R., & Talakua, M. (2021). Elementary students’ creative thinking skills in science in the Maluku islands, Indonesia. Creativity Studies, 14(1), 74–89. https://doi.org/10.3846/cs.2021.11244 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3846/cs.2021.11244
Malaysia Demographics 2020 (Population, Age, The current batch in the MMedPhys ex, Trends) – Worldometers 2019. (n.d.). https://Www.Worldometers.Info/Demographics/Malaysia-Demographics
Markus, S. (2019). The Programme for International Student.
MoE, M. of E. (2023). Digital Education Policy.
Mohd Yunos, M. A. A., Atan, N. A., Haruzuan Mohamad Said, M. N., Mokhtar, M., & Abu Samah, N. (2017). Collaborative learning in authentic environment apps to promote preschool basic scientific process skills. International Journal of Interactive Mobile Technologies, 11(3), 4–15. https://doi.org/10.3991/ijim.v11i3.5774 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3991/ijim.v11i3.5774
Nobari, A. D., Sarraf, M. H. K. M., Neshati, M., & Daneshvar, F. E. (2021). Characteristics of viral messages on Telegram; The world’s largest hybrid public and private messenger. Expert Systems with Applications, 168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2020.114303 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2020.114303
Oliver, E. (2016). A move towards heutagogy to empower theology students. HTS Teologiese Studies / Theological Studies, 72(1). https://doi.org/10.4102/hts.v72i1.3394 DOI: https://doi.org/10.4102/hts.v72i1.3394
Ong, J. S. H., Mohan, P. R., Han, J. Y., Chew, J. Y., & Fung, F. M. (2021). Coding a Telegram Quiz Bot to Aid Learners in Environmental Chemistry. Journal of Chemical Education, 98(8), 2699–2703. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jchemed.1c00201 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jchemed.1c00201
Ozdemir, G., & Dikici, A. (2017). www.jeseh.net Relationships between Scientific Process Skills and Scientific Creativity: Mediating Role of Nature of Science Knowledge. www.jeseh.net DOI: https://doi.org/10.21891/jeseh.275696
Prusak, N., & Hershkowitz, R. (2015). Nurturing students’ creativity through telling mathematical stories. 9th Mathematical Creativity and Giftedness International Conference Proceedings. Romania: Sinaia.
Redondo, R. P. D., Rodriguez, M. C., Torres-Guijarro, S., Silva, I. V., & Vazquez, M. M. (2021, June 7). A Micro Learning Approach Based on a Telegram Bot: A Gender-Inclusive Language Experience. 2021 10th Mediterranean Conference on Embedded Computing, MECO 2021. https://doi.org/10.1109/MECO52532.2021.9460187 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/MECO52532.2021.9460187
Saeed, B. A., & Ramdane, T. (2022). The effect of implementation of a creative thinking model on the development of creative thinking skills in high school students: A systematic review. Review of Education, 10(3). https://doi.org/10.1002/rev3.3379 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/rev3.3379
Selvaraj, A., Radhin, V., KA, N., Benson, N., & Mathew, A. J. (2021). Effect of pandemic based online education on teaching and learning system. International Journal of Educational Development, 85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijedudev.2021.102444 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijedudev.2021.102444
Shadish, W. R., Cook, T. D., & Campbell, D. T. (2002). Experimental And Quasi-Experimental Designs for Generalized Causal Inference.
Sustainable Development Report. (2024). Statistical Performance Index Missing Data in SDG Idex. https://sdgs.un.org
Tang, Y. M., Chen, P. C., Law, K. M. Y., Wu, C. H., Lau, Y. yip, Guan, J., He, D., & Ho, G. T. S. (2021). Comparative analysis of Student’s live online learning readiness during the coronavirus (COVID-19) pandemic in the higher education sector. Computers and Education, 168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2021.104211 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2021.104211
Telegram Official Website,. (2021). ( Https://Telegram.Org/Faq#q-What-Is-Telegram-What-Do-i-Do-Here).
Topal, A. D., Eren, C. D., & Geçer, A. K. (2021). Chatbot application in a 5th grade science course. Education and Information Technologies, 26(5), 6241–6265. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-021-10627-8 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-021-10627-8
Yildiz, C., & Yildiz, T. G. (2021). Exploring the relationship between creative thinking and scientific process skills of preschool children. Thinking Skills and Creativity, 39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tsc.2021.100795 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tsc.2021.100795
Yılmaz, A. (2021). The effect of technology integration in education on prospective teachers’ critical and creative thinking, multidimensional 21st century skills and academic achievements. Participatory Educational Research, 8(2), 163–199. https://doi.org/10.17275/per.21.35.8.2 DOI: https://doi.org/10.17275/per.21.35.8.2
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
Categories
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Abdullah Abdul Halim, Noor Dayana Abd Halim

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.









